Decellularization and Dissection
Isolating the extracellular matrix
In the lab, we utilize lung extracellular matrix (ECM) to create physiologically relevant environments. This advances our understanding of cellular behaviors in the lungs. To do this, we work with both diseased and healthy human, pig, and small animal lungs. Over the years, the Weiss Lab has developed a standardized method of decellularization. This removes all cellular material and leaves behind the scaffold, microstructures, and ECM. To use the whole organ for research, we carefully dissect each lung into four distinct tissue categories: airway, alveolar, bulk, and vasculature. Once dissected, we proceed to lyophilize, cryo-mill, and pepsin digest each sample, resulting in the final ECM material.
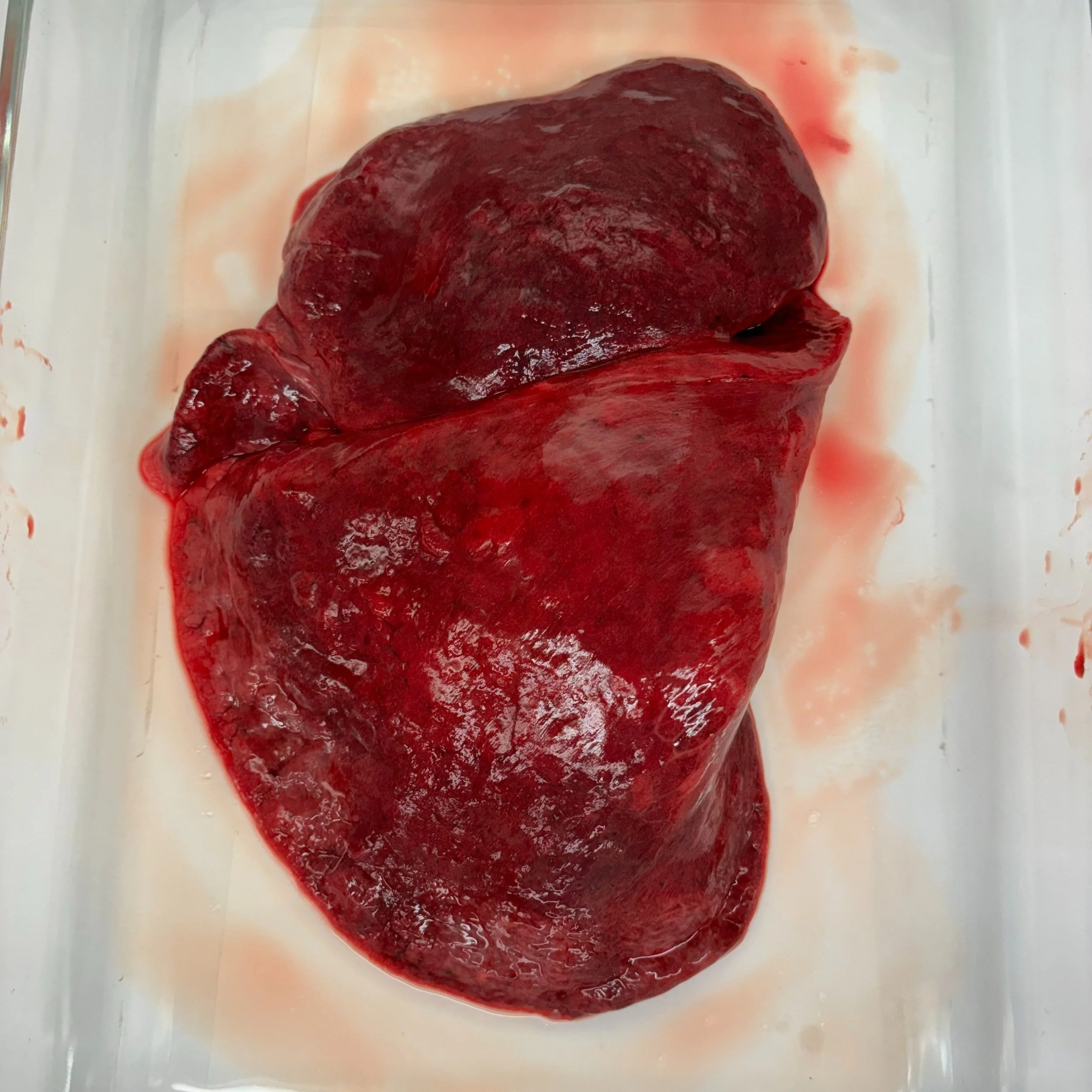
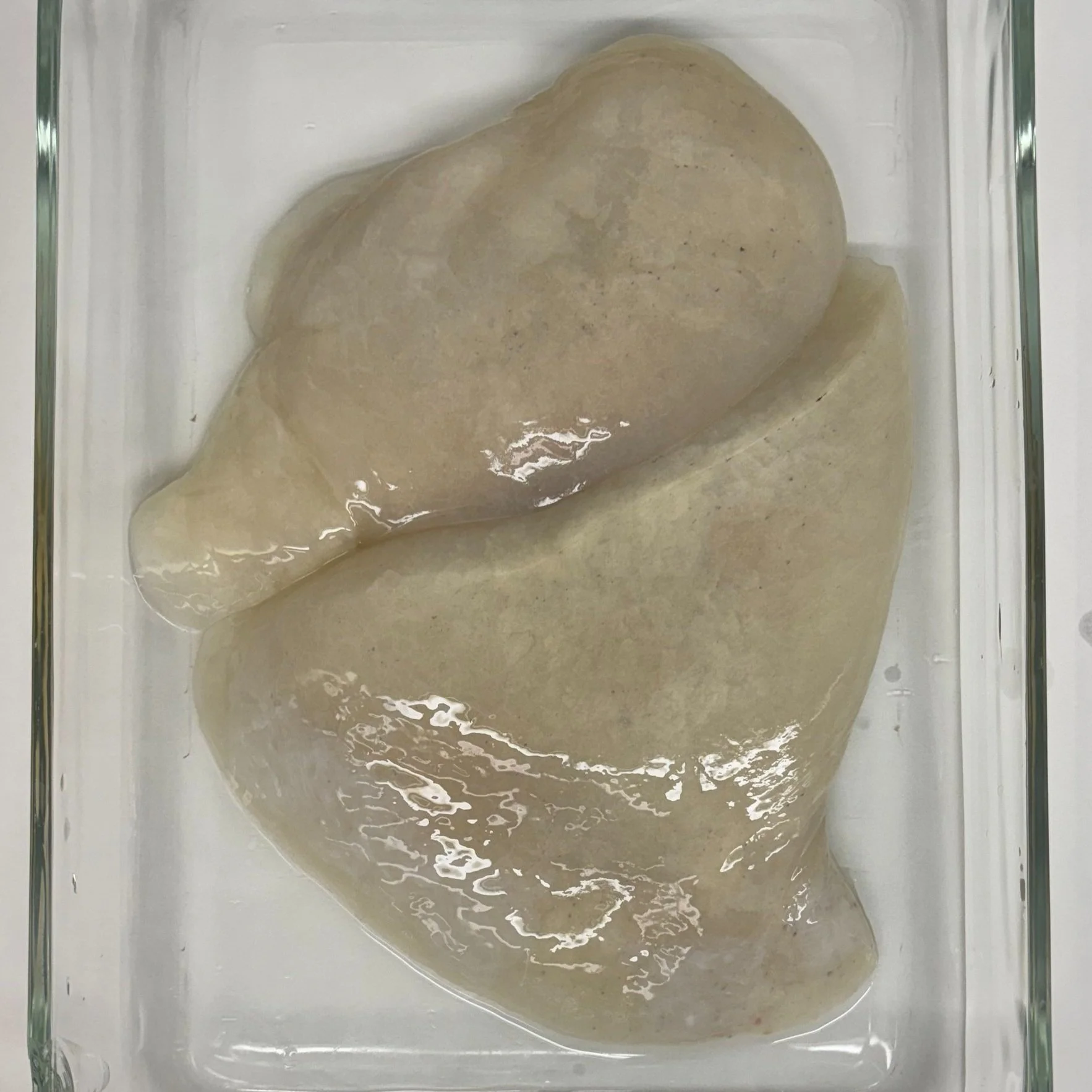
Healthy Human Lung Decellularization
Healthy Human Lung Dissection
-
Branching cartilaginous structure, which allows airflow during ventilation.
-
Region of gas exchange within lung.
-
Connective tissue and non-distinguishable sections of the lung.
-
Blood vessel network within the lung.
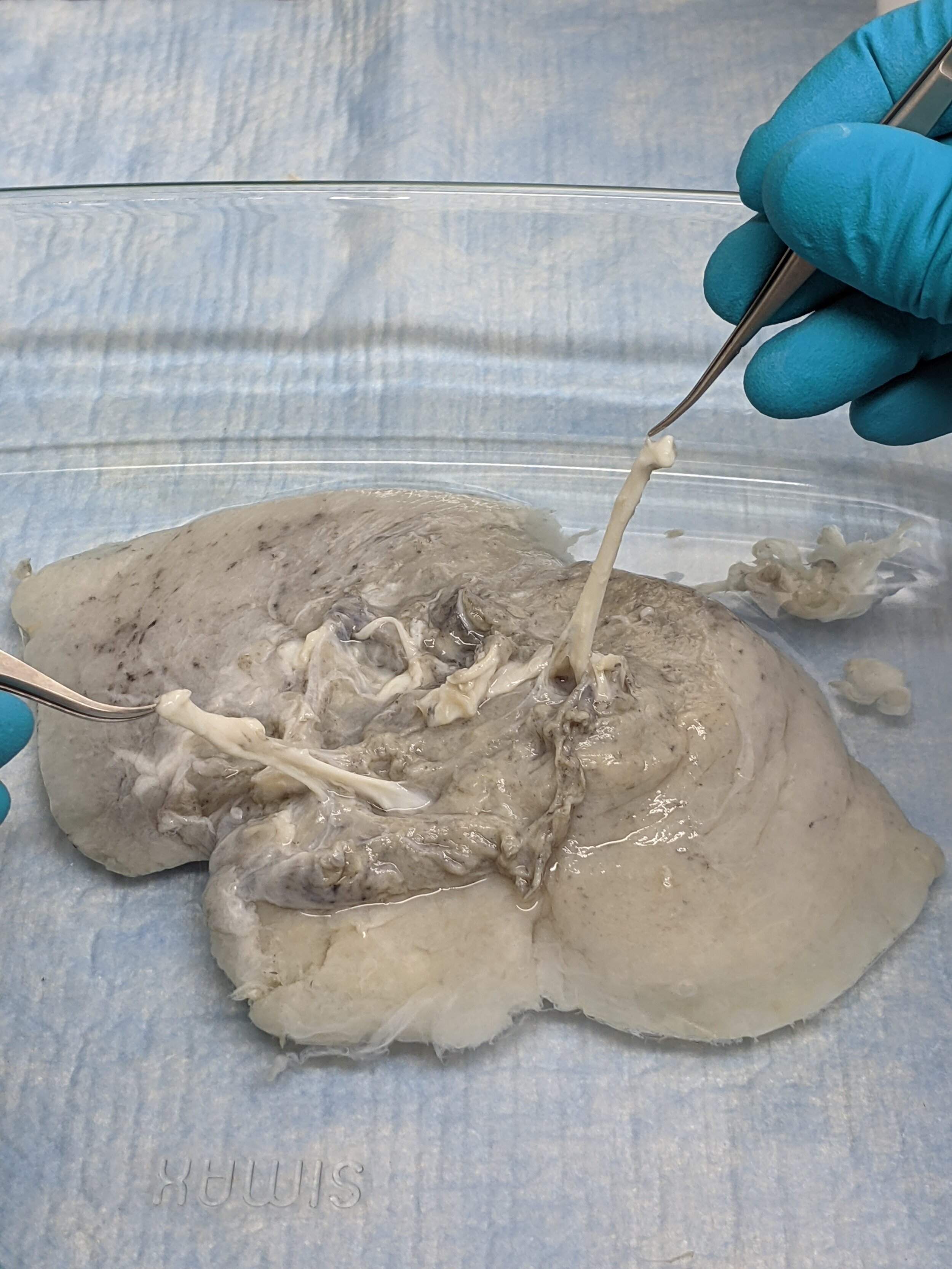
Here, former lab members Brad and Isaac hold two pieces of lung tissue in forceps. These white strands are some of the lung's vasculature.

Here, a section of vasculature is being held tightly between two forceps, demonstrating its opaque white appearance and elastic properties.

In this image, we have resected a sizable region of vasculature and are about to sever a portion of it.

This image shows the portion of vasculature that was severed in the previous image.

Here we opened up the superior end of an airway branch providing a good visual.
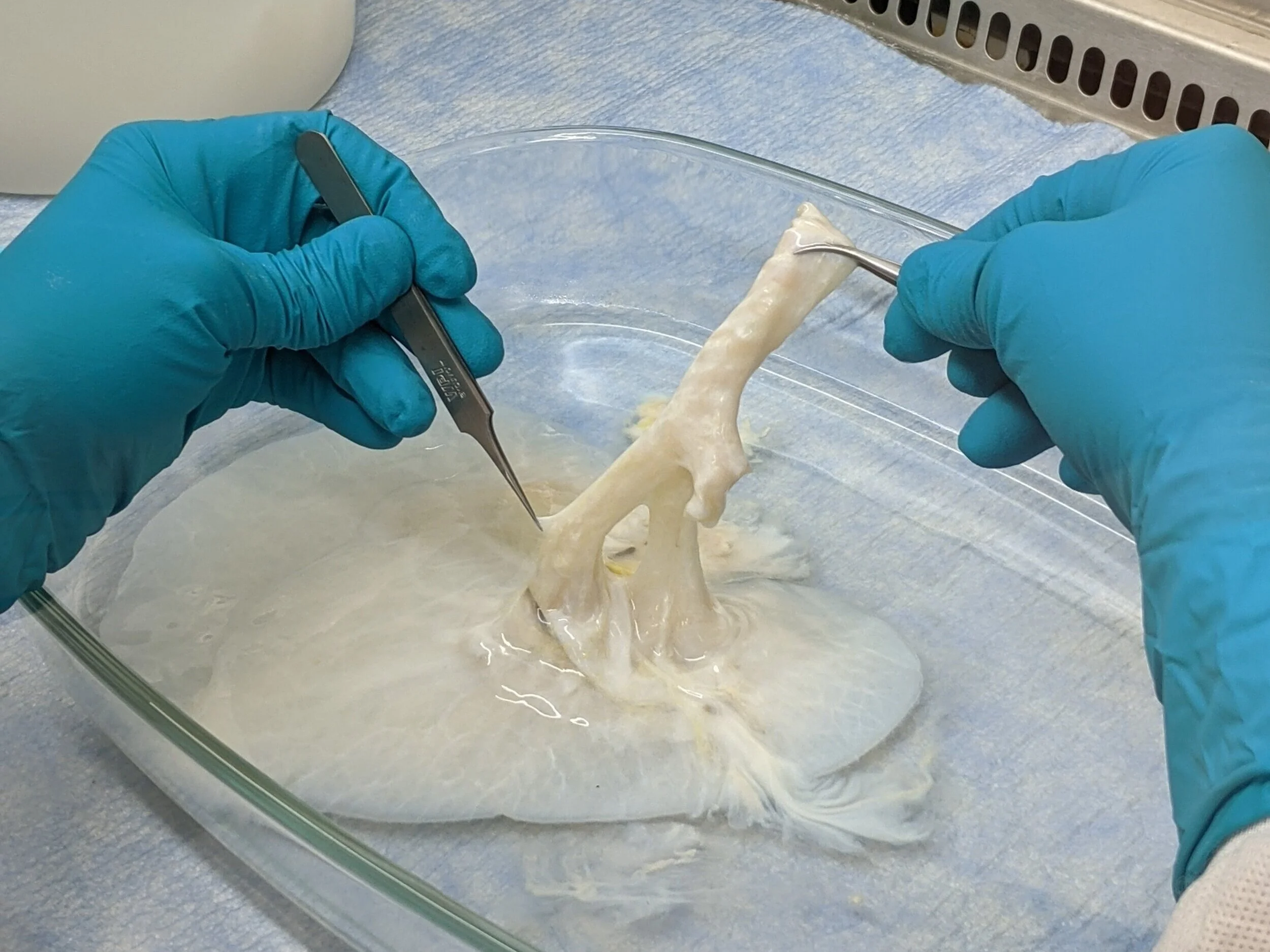
In the image above, the upper airway region is being held by two forceps. Descending from the right pair of forceps, several cartilage rings are visible along the surface of the airway. These rings appear white while the remaining sections of the airway are an off-white, tan-ish color.

To help determine the airway's routing within the lobe, we have carefully inserted one arm of a pair of forceps into a descending path.